Thresholding
For colored shape detection, we want to tune our HSV thresholds such that only the goal color remains after the thresholding. The HSV color representation is similar to RGB in that it represents colors. However, HSV represents colors with hue, saturation and value components. Hue refers to the color, while saturation and value describe its richness and brightness.
In PhotonVision, HSV thresholds is available in the “Threshold” tab.
Color Picker
The color picker can be used to quickly adjust HSV values. “Set to average” will set the HSV range to the color of the pixel selected, while “shrink range” and “expand range” will change the HSV threshold to include or exclude the selected pixel, respectively.
Tuning Steps
The following steps were derived from FRC 254’s 2016 Championship presentation on computer vision and allows you to accurately tune PhotonVision to track your target.
In order to properly capture the colors that you want, first turn your exposure low until you have a mostly dark image with the target still showing. A darker image ensures that you don’t see things that aren’t your target (ex. overhead lights). Be careful not to overexpose your image (you will be able to tell this if a target looks more cyan/white or equivalent instead of green when looking at it through the video feed) since that can give you poor results.
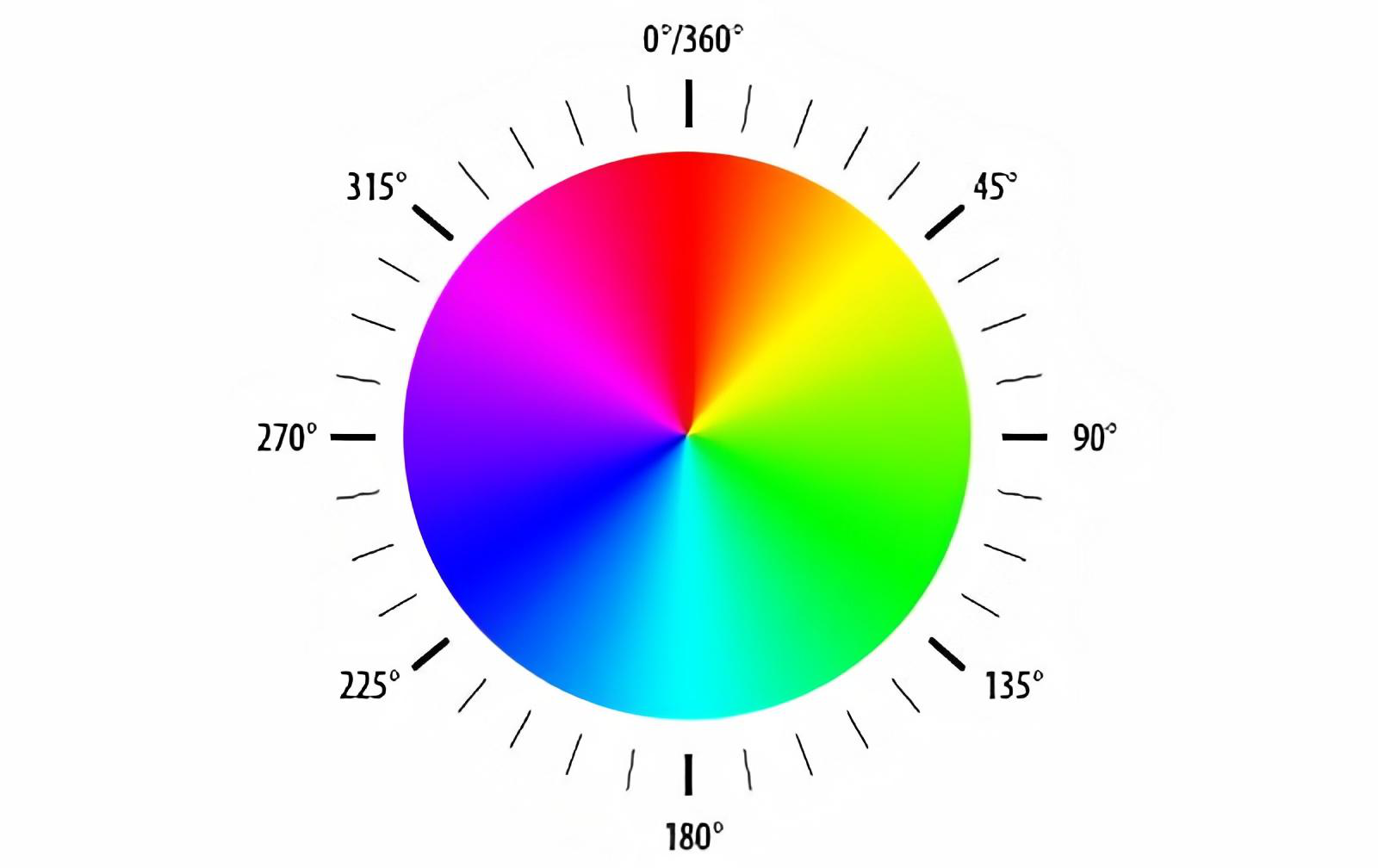
For HSV tuning, start with Hue, as it is the most important/differentiating factor when it comes to detecting color. You want to make the range for Hue as small as possible in order to get accurate tracking. Feel free to reference the chart below to help. After you have properly tuned Hue, tune for high saturation/color intensity (S), and then brightness (V). Using this method will decrease the likelihood that you need to calibrate on the field. Saturation and Value’s upper bounds will often end up needing to be the maximum (255).